 |
| Dynamic observation of silicate nanoparticles in water |
.PNG)  |
| Dynamic observation of polystyrene beads under various media |
.PNG) |
| ( Anal. Chem. 2012, 84: 6312 −6316 ) |
 |
K-kits allow direct observation of nanoparticles in blood. Simply place K-kit channel in contact with whole blood sample without any pretreatment, serum will be loaded into the channel by capillary effect. |
 |
Image-based statistic analysis of Particle Concentration (K-kit vs. ICP-MS) |
 |
| Image-based statistic analysis of aggregation and agglomeration of AuNPs in blood |
|
 |
| For liquid food and food supplements, K-kits allow direct observation of nanoscale objects in final product form. |
|
 |
| The statistical analysis of CaCO3 nanoparticles in milk. |
 |
| K-kit can be used for characterizing NOAAs in cosmetics in final product forms, including lotion, cream, and powder, to assess the safety risks of nanomaterials in cosmetic ingredients. |
.PNG) |  |
| Protein particles (Paclitaxel@Albumin) in Abraxane® | |
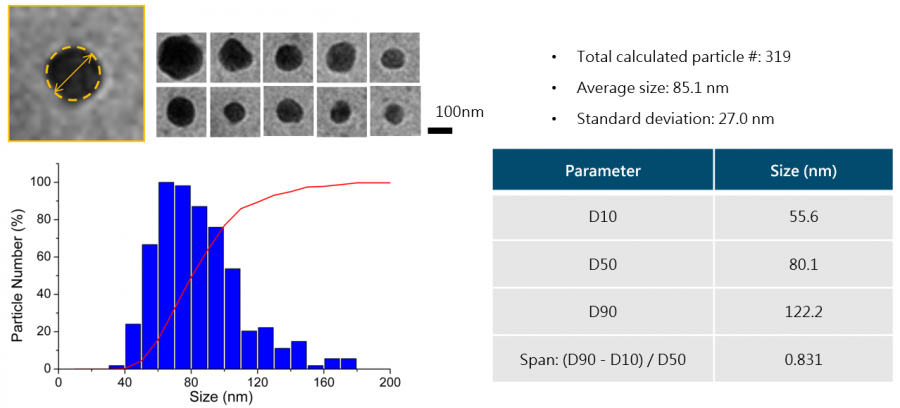 | |
| Abraxane in saline _ size & size distribution (D10/ D50/ D90) | |
K-kit can be used for characterizing protein particles in Nanopharmaceuticals by imaging the particle morphology, size and size distribution, to evaluate drug formulation or conduct any bioequivalence study. | |
 | A micelle or micella (plural micelles or micellae, respectively) is an aggregate (or supramolecular assembly) of surfactant molecules dispersed in a liquid colloid. A typical micelle in aqueous solution forms an aggregate with the hydrophilic "head" regions in contact with surrounding solvent, sequestering the hydrophobic single-tail regions in the micelle centre. |
| |
 In K-kit (Magn. x 10K) |  On Cu grid (Magn. x 10K) |
| |
| | |
 In K-kit (Magn. x 20K) |  On Cu grid (Magn. x 20K) |
| |
| | |
K-kit can be used for characterizing micelle particles in liquid, by imaging the particle morphology, size and size distribution. | |